Selectivity or Invariance: Boundary-aware Salient Object Detection
Jinming Su1,3 Jia Li1,3,* Yu Zhang1 Changqun Xia3 Yonghong Tian2,3,*
1State Key Laboratory of Virtual Reality Technology and Systems, SCSE, Beihang University 2National Engineering Laboratory for Video Technology, School of EE&CS, Peking University 3Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen, ChinaPublished in ICCV, 2019
Abstract
Typically, a salient object detection (SOD) model faces opposite requirements in processing object interiors and boundaries. The features of interiors should be invariant to strong appearance change so as to pop-out the salient object as a whole, while the features of boundaries should be selective to slight appearance change to distinguish salient objects and background. To address this selectivity-invariance dilemma, we propose a novel boundary-aware network with successive dilation for image-based SOD. In this network, the feature selectivity at boundaries is enhanced by incorporating a boundary localization stream, while the feature invariance at interiors is guaranteed with a complex interior perception stream. Moreover, a transition compensation stream is adopted to amend the probable failures in transitional regions between interiors and boundaries. In particular, an integrated successive dilation module is proposed to enhance the feature invariance at interiors and transitional regions. Extensive experiments on six datasets show that the proposed approach outperforms 16 state-of-the-art methods.
Method
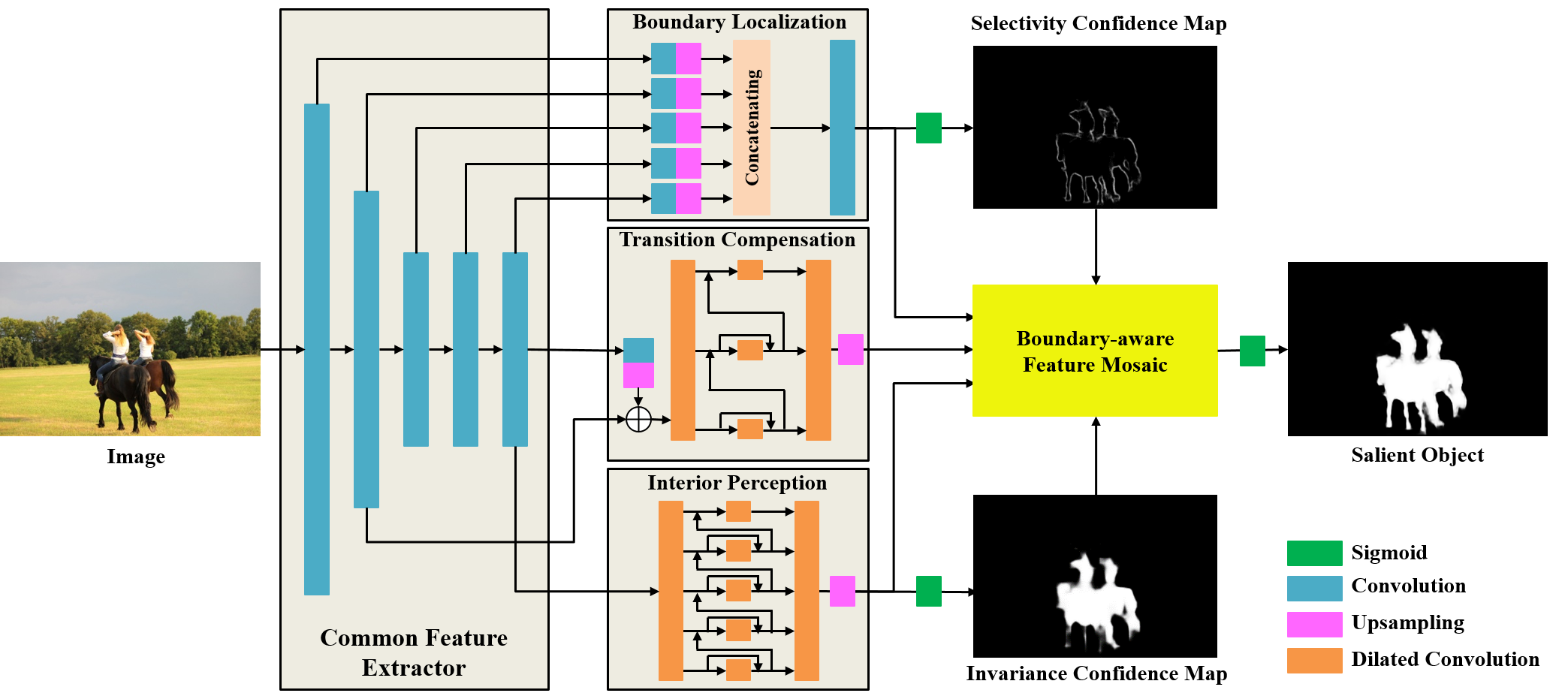
The framework of our approach. We first use ResNet-50 to extract common features for three streams. The boundary localization stream uses multi-level features and a simple network to detect salient boundaries with high selectivity, while the interior perception stream uses single-level features and a complex network to guarantee invariance in salient interiors. Their output features are used to form two confidence maps of selectivity and invariance, based on which a transition compensation stream is adopted to amend the probable failures that are likely to occur in the transition regions between boundaries and interiors. These three streams are concatenated to form a boundary-aware feature mosaic map so that the salient object can pop-out as a whole with clear boundaries.
Quantitative Evaluation
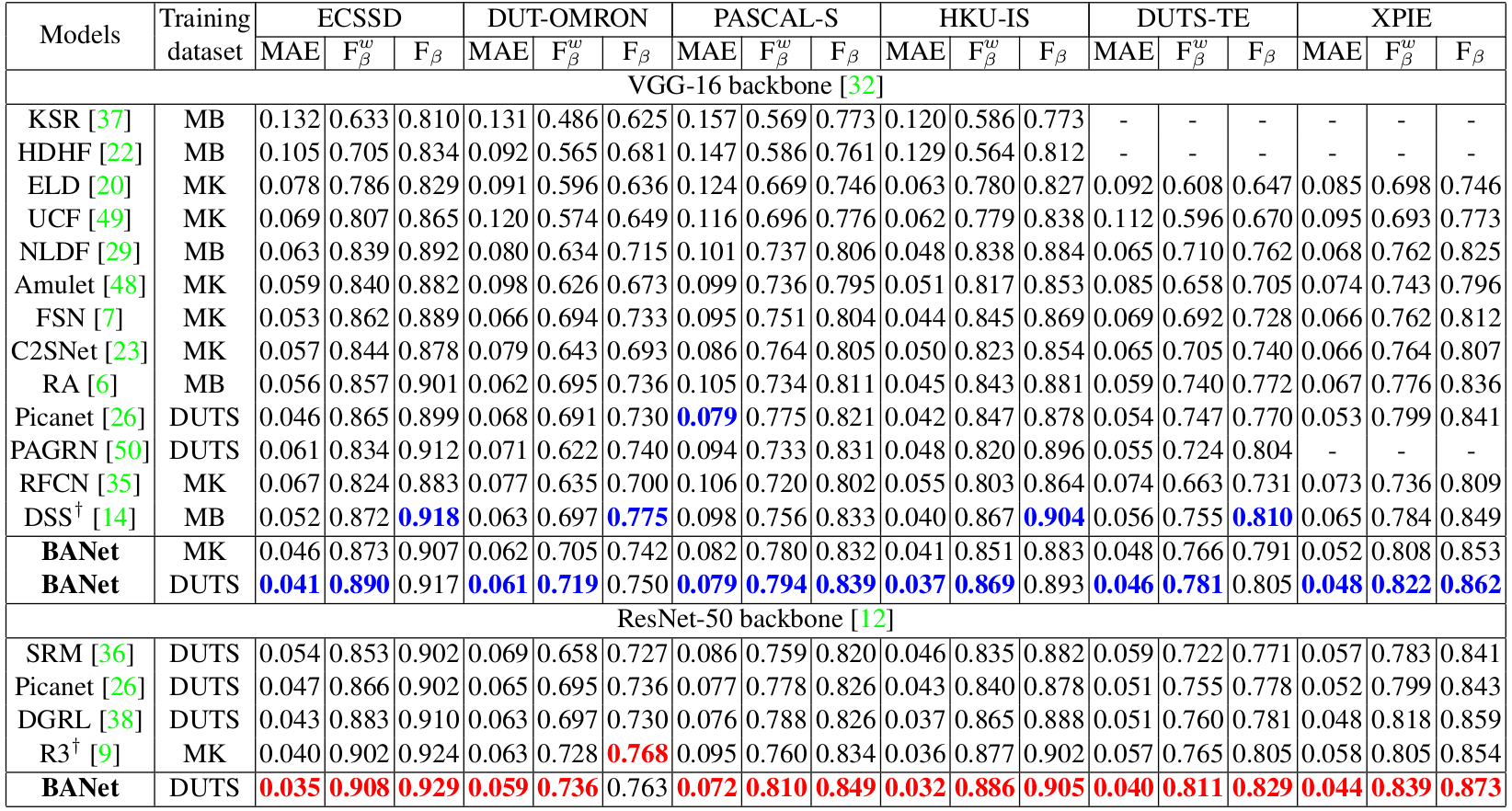
Performance of 16 state-of-the-arts and the proposed method on six benchmark datasets. Smaller MAE, larger Fwβ and Fβ correspond to better performance. The best results of different backbones are in blue and red fonts. "-" means the results cannot be obtained and "†" means the results are post-processed by dense conditional random field (CRF). Note that the backbone of PAGRN is VGG-19 and the one of R3Net is ResNeXt-101. MK: MSRA10K, DUTS: DUTS-TR, MB: MSRA-B.
Qualitative Evaluation
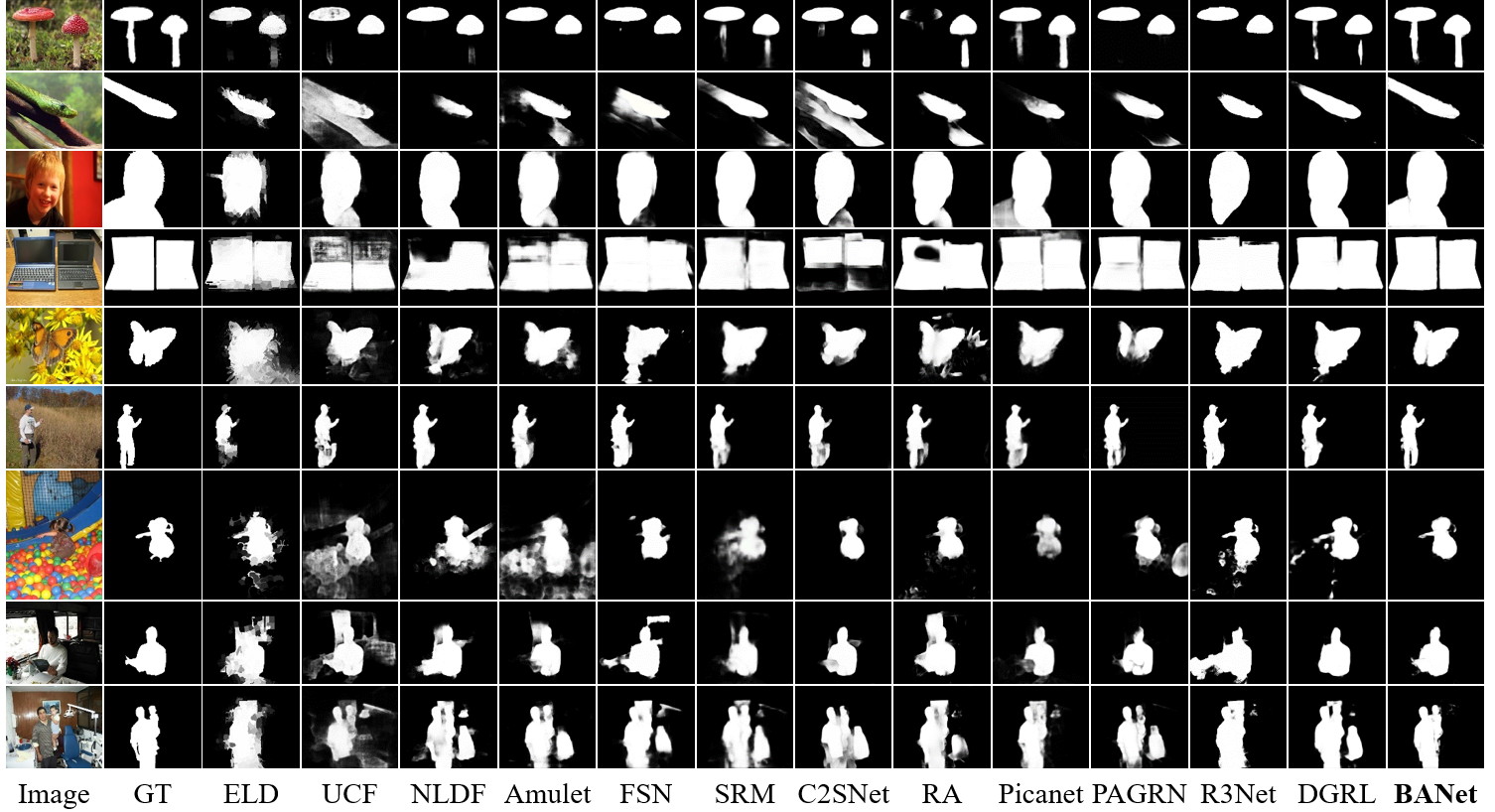

Qualitative comparisons of the state-of-the-art algorithms and our approach. GT means ground-truth masks of salient objects. The images are selected from six datasets for testing.
Citation
Jinming Su, Jia Li, Yu Zhang, Changqun Xia, Yonghong Tian. Selectivity or Invariance: Boundary-aware Salient Object Detection. In ICCV, 2019.
Paper: [PDF]
Resources:
Results on ECSSD, DUT-OMRON, PASCAL-S, HKU-IS, DUTS-TE, XPIE:[Results of ResNet. 317MB] [Results of VGG. 310MB] [Code & model. 203MB] Results on SOD:
[Results.]
BibTex:
@inproceedings{su2019banet,
title={Selectivity or Invariance: Boundary-aware Salient Object Detection},
author={Su, Jinming and Li, Jia and Zhang, Yu and Xia, Changqun and Tian, Yonghong.},
booktitle={ICCV},
year={2019}
}